


2024-03-29
Whether in the new energy automobile industry or the electronic and electrical industry, thermal conductive materials are widely used. In thermodynamics, thermal conductivity is an important parameter that reflects the heat conduction performance of materials, and it is also a technical indicator that users are more concerned about. Today, You Xingsha will introduce to you the testing method of thermal conductivity.

What is thermal conductivity?
Thermal conductivity, also called thermal conductivity, refers to the amount of heat passing through a given material cross-section per unit time, which is proportional to the rate of temperature change perpendicular to the cross-section and the cross-sectional area. The direction of heat transfer is opposite to the direction of temperature increase.
Thermal conductivity is a physical quantity that expresses the thermal conductivity of a material.
Test method for thermal conductivity
(1) Steady-state method: plate method, heat flow meter method;
(2) Unsteady-state methods: transient hot-line method, transient plane heat source method, probe method, laser method, and 3ω method.
At present, there is no unified thermal conductivity testing standard for domestic and foreign markets. For the thermal conductivity of new energy thermal conductive materials, the most recognized test method in the industry is ASTM D5470 of the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). This standard is published under the fixed name D5470. (ASTM D5470-17 was published in November 2017, and the suffix number indicates the year of original adoption or, in the case of revisions, the year of last revision.)
This standard uses the steady-state heat flow method, which is a test method for the heat transfer of thin thermally conductive solid electrical insulation materials. It is relatively better at simulating actual usage conditions and reflecting thermal conductivity, and is particularly suitable for measuring the thermal conductivity of thermally conductive materials under actual usage conditions, as well as measuring various thermal contact materials and contact thermal resistance.
Principle of steady-state heat flow meter method
The steady-state heat flow method tests the thermal conductivity of materials based on the principle of Fourier's law. During the test, a constant heat flow and pressure are applied to the sample, and the temperature difference between the upper and lower surfaces of the sample between the hot plate/cold plate is measured to obtain the thermal conductivity of the sample.
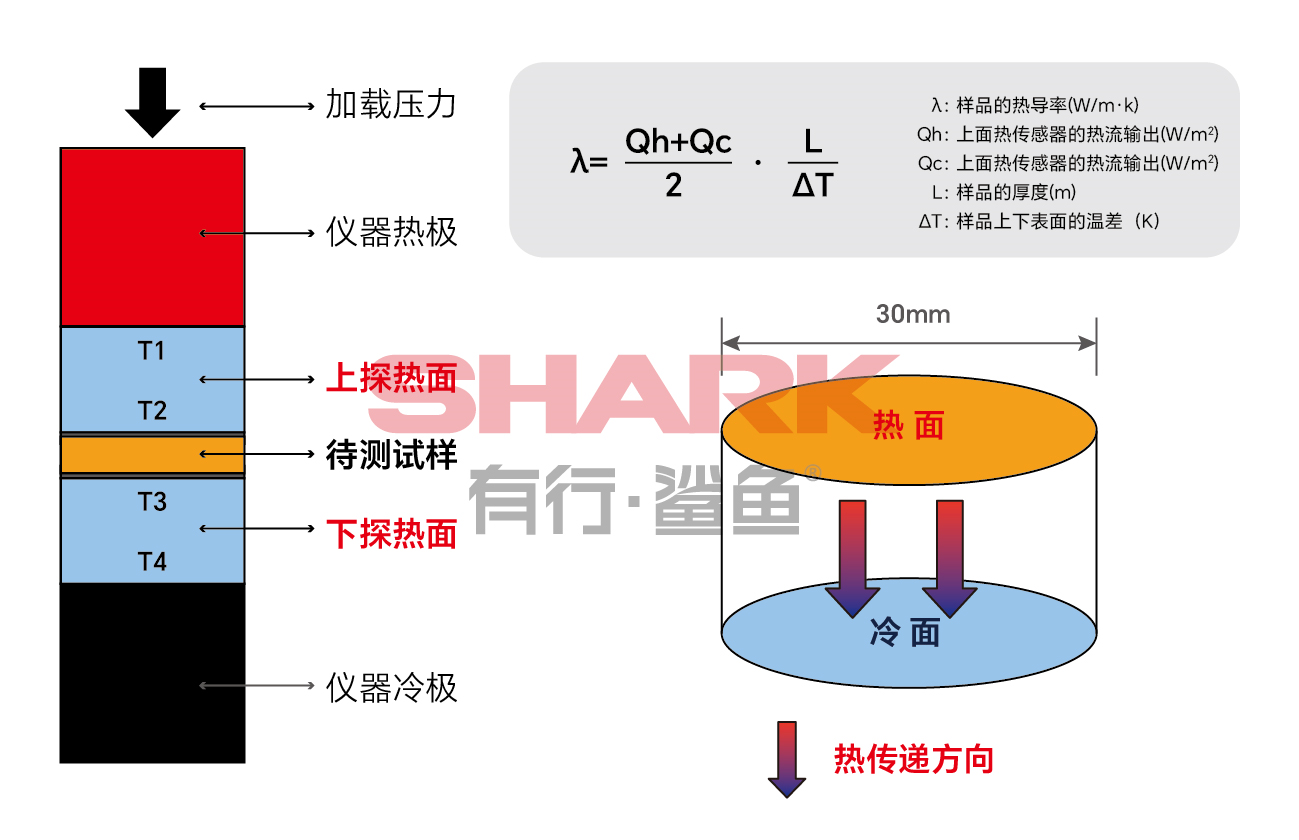
SY-2961 thermal conductivity test case
We take Youxingshark thermally conductive structural adhesive SY-2961 as an example. Using the ASTM D5470-17 test method, the following data can be measured:
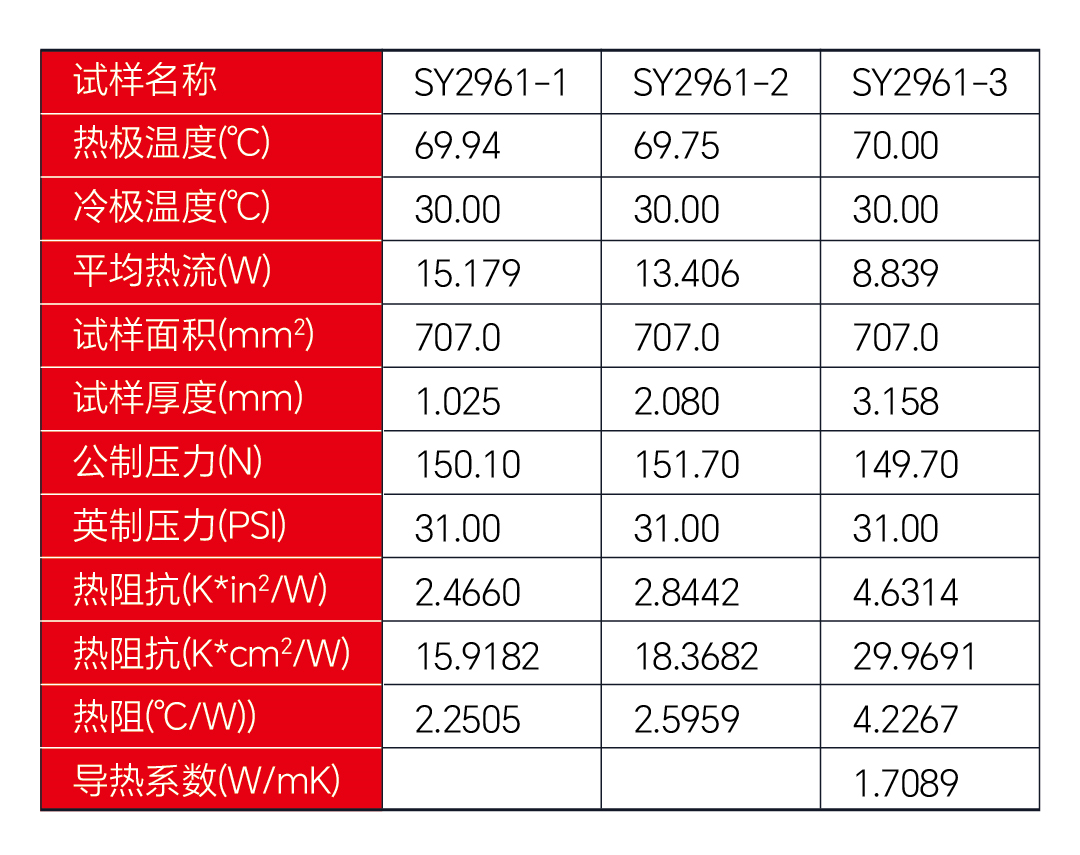
Conclusion: According to the corresponding conditions and requirements, the thermal conductivity of Youxingshark thermally conductive structural adhesive SY-2961 was measured to be approximately 1.70W/m·K.